|
| | CAP Overview | CAP Research | |
|
 |
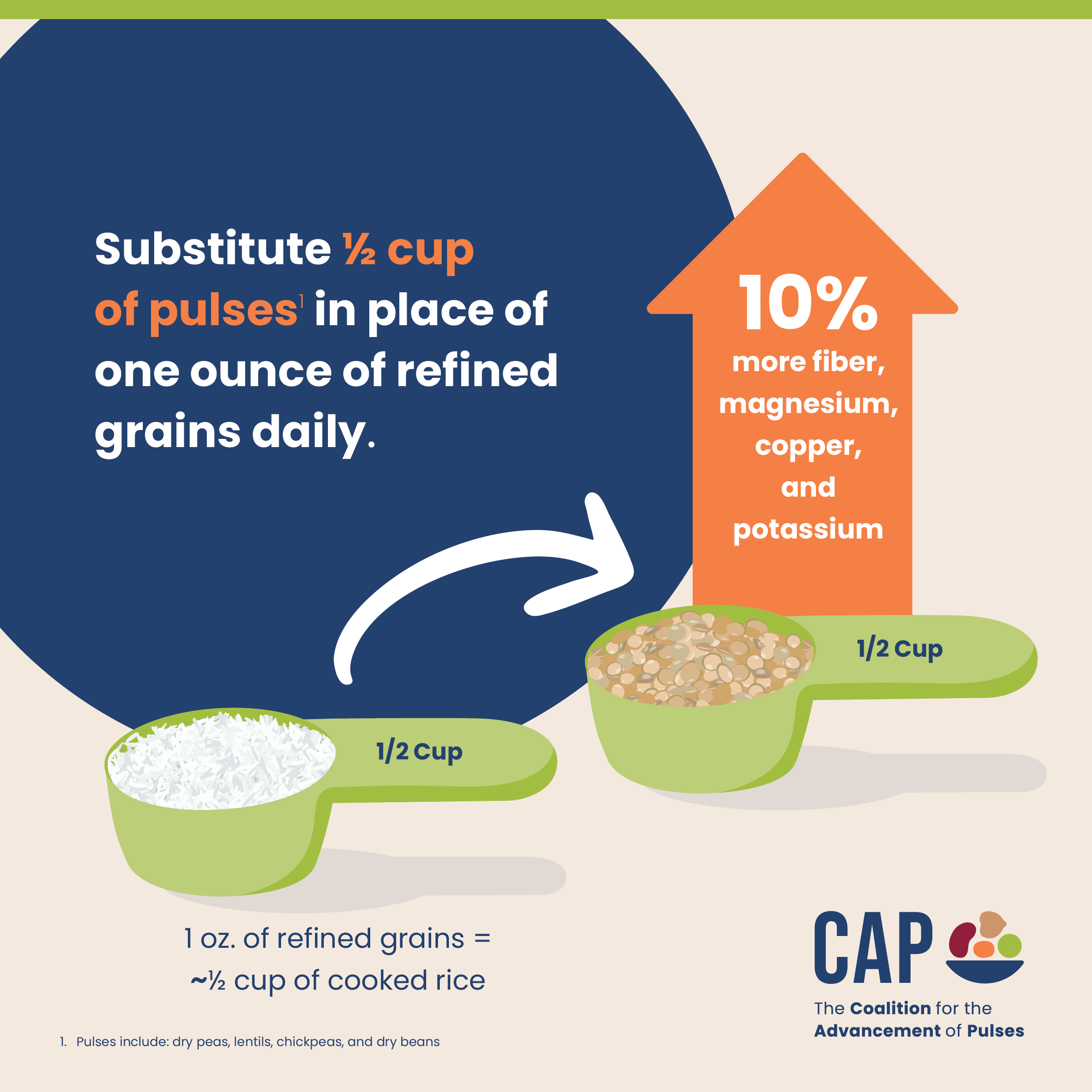
Swapping Pulses for Common Proteins
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Eating Beans and Chickpeas is Linked to Better Diet Quality
|
|
|
|
|
| PRESS RELEASE READ THE STUDY |
Adding Pulses can Lead to Improved Shortfall Nutrient Intakes and a Higher Diet Quality in American Adults |
|
|
A study published in Maturitas highlights the health benefits of eating more pulses, like beans and chickpeas, to improve diet quality. Using data from the National Health and Examination Survey (NHANES), researchers found that adding one or two servings of beans or chickpeas to typical American diets significantly increased the intake of key shortfall nutrients, such as fiber, potassium, and iron, and improved overall diet quality by up to 20%. The study emphasizes that most adults are not consuming enough pulses, which are essential for filling nutrient gaps and preventing chronic diseases like heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. The Healthy Eating Index showed that higher diet quality scores are associated with a reduced risk of cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. The research underscores the importance of including pulses in daily diets for both younger and older adults.
|
|
Pulse Consumption Linked to Reduced Risk of Type 2 Diabetes and Heart Disease |
|
 A scoping review published in Nutrients highlights the health benefits of pulses, such as beans, lentils, and chickpeas, in managing Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) and improving cardiovascular health. The review examined 30 studies and found that pulse consumption improves key cardiovascular biomarkers, including LDL and HDL cholesterol levels, and supports better glycemic control. Pulses were shown to lower the risk of heart disease and improve insulin sensitivity, offering potential benefits for people with diabetes. Additionally, the review emphasizes pulses’ role in reducing inflammation and oxidative stress. These findings support dietary guidelines that promote increased pulse consumption as part of a healthy diet. A scoping review published in Nutrients highlights the health benefits of pulses, such as beans, lentils, and chickpeas, in managing Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) and improving cardiovascular health. The review examined 30 studies and found that pulse consumption improves key cardiovascular biomarkers, including LDL and HDL cholesterol levels, and supports better glycemic control. Pulses were shown to lower the risk of heart disease and improve insulin sensitivity, offering potential benefits for people with diabetes. Additionally, the review emphasizes pulses’ role in reducing inflammation and oxidative stress. These findings support dietary guidelines that promote increased pulse consumption as part of a healthy diet. |
|